OLED技术一览
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. OLED light technology, unlike OLED displays, is mainly used for general lighting and automotive applications. For these applications, it is favorable due to its homogeneous light emission and ultra-thin, lightweight form factor, among other things.

OLED 技术可用于构建固态照明 (SSL),它由夹在两个电极之间的薄碳基有机层组成。当施加直流电时,空穴和电子分别从阳极和阴极注入有机层,在有机分子上形成激发态。当处于激发态的激子跃迁回基态时,会发生电致发光并发出光。
发光颜色或波长由形成激发态的有机分子的结构决定。对 OLED 技术而言,有多种光色可供选择。而 OLED 照明则是经过严格筛选的有机物的混合体,以实现所需的白光光谱。
The color or wavelength of the emitted light is determined by the structure of the organic molecule that forms the excited state. In OLED technology, a variety of emission colors are available, but for OLED lighting, the mixture of organics is carefully selected to shape the resulting spectrum of emitted white light.
OLED 照明面板包括提供机械结构和所需光学特性的透明基底。基底包含图案化的透明导电层,通常是氧化铟锡 (ITO),用作底部电极或阳极。超薄的有机材料层沉积在阳极表面,然后是金属阴极或第二电极。整个 OLED 层比人的头发丝还细,每一层都包含多种有机材料。
An OLED lighting panel starts with a transparent substrate that provides both the mechanical structure and the desired optical properties. The substrate contains a patterned transparent conductive layer, usually indium tin oxide (ITO), which serves as the bottom electrode or anode. Very thin layers of organic materials are deposited on the anode surface, followed by a metallic cathode or second electrode. The entire OLED stack is thinner than a human hair and each layer can contain several organic materials.
Unlike inorganic LEDs, the organic materials are disordered and do not need to form single crystals or be deposited on expensive crystalline substrates for efficient emission. Therefore, the emission area with OLED lighting can cover most of the substrate and provides a wide, low glare light source with no hot spots, ideal for large area light sources. The wide, flat emission of OLED lighting also offers the ability to selectively target specific areas of the panel with high contrast when the electrodes are patterned, providing an additional layer of communication through movement, customization and branding with light.
#OLED 的优点
Some advantages of OLEDs


# OLED 与 LED
OLED vs LED
相比之下,OLED 发光面板本质上是均匀且无眩光的,因此 OLED 发光面板的能效与提供的光效率相匹配。这种影响非常显著,以至于在某些应用中,OLED 照明解决方案比 LED 照明解决方案更均匀、更节能。
LEDs are tiny, highly concentrated light sources thatare suited for producing intense beams of light required in car headlights,headlamps, torches and other high-intensity, focused lighting applications. Tomake LEDs useful for automotive interior lighting or other low-intensityapplications, the LED light must be diffused, scattered and homogenized, whichreduces the energy efficiency of the light ultimately delivered.
In contrast, OLED light panels are inherentlyhomogeneous and glare-free, so the energy efficiency of OLED light panelsmatches the light efficiency delivered. This effect is so significant that insome applications, the OLED lighting solution is both more homogeneous and moreenergy efficient than the LED lighting solution.
#OLED 照明与 OLED 显示
OLED Lighting vs OLED Display
OLED 显示和 OLED 照明均基于相同的固态物理原理。OLED 技术由有机半导体材料组成,通电时会发光。 OLED 材料可直接发射全波长范围的光,不需要荧光粉转换来获得所需的光谱。
OLED 的光品质满足以下两种应用。在照明方面,自然漫射光束将 OLED 灯具定位为无眩光的全彩体验,以实现视觉舒适。对于显示领域,直接全彩输出可实现包括真黑在内的高色域。
The light quality of OLED fulfils both applications. For illumination, the naturally diffuse light beam positions OLED luminaires as a glare-free full color experience for visual comfort. For display, the direct color output enables a high color gamut including true black.
作为一种功能性的光源,OLED可提供发光均匀、较大发光面、较高亮度的白光照明。灯具的使用寿命通常超过10年。相比之下,显示器通常亮度较低,作为单独寻址的红、绿、蓝 (RGB) 像素运行,寿命较短。显示器传输图像、视频和消息,通常以非常高的刷新率运行 (>120Hz)。
As a functional light source, OLEDs work as a uniform, large area, high brightness, white spectrum light engine. The service life of the lighting usually exceeds 10 years. Displays, by comparison, typically have a fraction of the brightness and operate as individually addressed red, green, blue (RGB) pixels that have a shorter life. Displays transmit images, videos and messages - usually at very high image data rates (>120Hz).
#OLED显示与照明的区别总结
Summary of the differences between OLED display and illumination
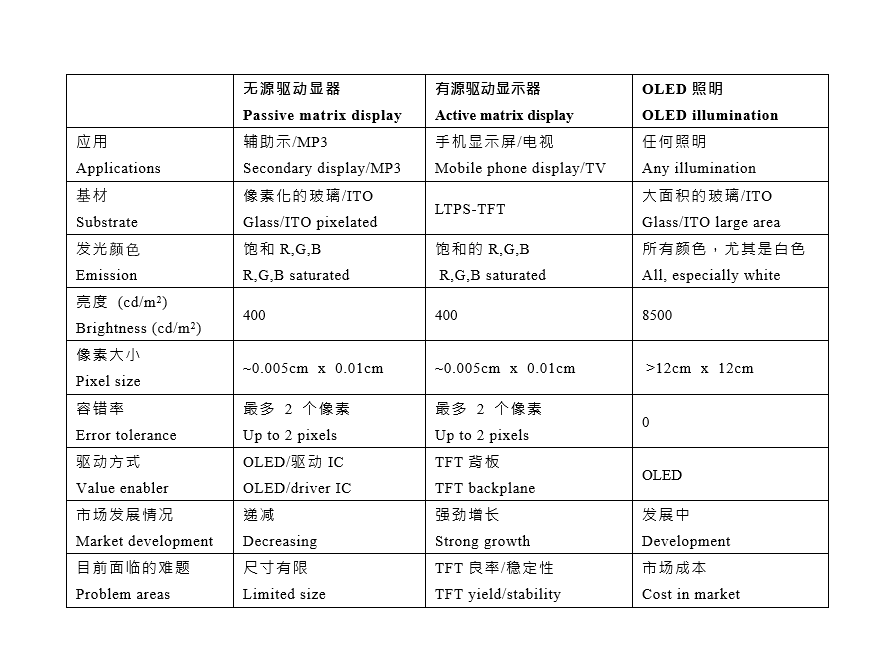
与 OLED 显示器不同,OLED 灯具针对照明进行了优化,因此 OLED 灯具比 OLED 显示器更亮(OLED 灯具为 8,000 nit,而 OLED 显示器的亮度低于 1,000 nit)。OLED 灯具的使用寿命也比 OLED 显示器长得多。与 OLED 显示器相比,OLED 照明在连续使用超过 100,000 小时后会降至初始亮度的 70%,而同期 OLED 显示器从低得多的初始亮度降至 50%。
此外,OLED 灯具的设计和制造具有成本效益,OLED 照明面板成本已非常优异,而OLED 显示器价格则居高不下。OLED 显示器的高帧率使其非常适合通过电话屏幕和电视显示图像、视频和消息。
Finally, OLED luminaires are designed and manufactured to be cost effective, with OLED lighting panels being more like an incandescent bulb than the high-end price of an OLED display. The OLED display's high frame rate capability makes it ideal for displaying images, videos and messages via phone screens and televisions.
#健康和舒适
Health and well-being
Exposure to high-intensity blue wavelengths is associated with macular degeneration and circadian rhythm disturbances, depending on the exposure time. Light sources such as fluorescent lamps, which are bright white and cool, and incandescent bulbs have a higher risk for damaging to your eyes.
OLEDs are inherently safe because they deliver all wavelengths of light, including blue light. OLEDs deliver the light levels you need at an intensity far below the risk of damage. This is validated by the IEC standard for the physiological risk of blue and infrared light - OLEDs pose no risk to skin or eyes and are considered free of all photobiological risks.
宽光谱 OLED 灯提供全色调色板,同时消除大多数人工照明解决方案的负面特性,如紫外线、眩光、阴影和闪烁。将 OLED 的亮度与其独有的柔软度相结合,可以改善环境并提供类似日光的光线,即使您整天坐在室内,一直如白天般感觉。
#可持续性
Sustainability
世界上将近20% 的电力用于照明。照明能源占全球温室气体的 6%,大约为 19 亿吨二氧化碳,约占全球所有乘用车排放量的70%(来源:联合国环境规划署)。通过使用节能照明——例如 OLED 照明——这些数值可以被显着降低。测试表明,OLED 照明效率正变得与 LED 一样高效,节能率高达 80% 。这说明与传统白炽灯泡相比,OLED照明的节能效果更加显著。此外,这种OLED光源的制造过程非常高效。
OLED 灯具是面光源,无需漫射光的漫射屏。这有一个主要优势,因为使用传统光源时,系统会损失多达 70% 的光输出。采用OLED照明技术,光源的效率等于系统效率。此外,OLED 照明灯几乎 100% 由玻璃制成,可以在损坏后轻松回收。
#OLED的一些缺点
Some disadvantages of OLEDs
OLED 的使用寿命取决于温度:低初始光度但散热良好的 OLED(任何颜色)比从一开始就以最大光度运行而无散热的OLED 具有更长寿命,这是因为在较高温度下OLED材料的扩散发生得更快。
OLED 的另一个缺点是,与LED相比,市售 OLED 的发光效率仅为 40 lm/W - 60 lm/W范围内。OLED的实验室测试光效最高仅能达到略高于 100 lm/W ,而发光二极管的实验室测试值可达200 lm/W。
The service life of OLEDs is temperature-dependent: A well-cooled OLED (of any color) with a low initial luminosity always has a longer life than an OLED that is operated at maximum luminosity from the start without cooling. This is due to diffusion processes in the OLED that occur more quickly at higher temperatures.
Another disadvantage of OLEDs is the lower luminous efficacy in the range of 40 lm/W to 60 lm/W of commercially available OLEDs compared to light-emitting diodes. Peak values of selected laboratory samples of OLEDs achieve values just above 100 lm/W. Light-emitting diodes achieve laboratory values of 200 lm/W.
除了寿命较短和发光效率较低之外,OLED还易与某些外部物质发生反应。除了由于潮湿而无处不在的水汽之外,渗透的氧气也会破坏有机材料。因此,将显示器密封并保护其免受外部影响非常重要。必要的刚性封装削弱了其灵活性。高活性的钙和钡注入层尤其容易受到氧气的腐蚀。被腐蚀的典型迹象是圆形、不断增大的暗区,即所谓的“黑点”。原因通常是金属层气相沉积过程中的颗粒污染。多层结构的微观边缘也被腐蚀渗透,导致显示屏中有效发光像素面积的减少。
In addition to shorter life and lower luminous efficacy, OLEDs also react sensitively to certain external substances. In addition to water, which is omnipresent due to humidity, penetrating oxygen can also destroy the organic material. It is therefore important to hermetically encapsulate the display and protect it from external influences. The necessary rigid encapsulation impairs flexibility. The highly reactive injection layer of calcium and barium is especially endangered by corrosion with oxygen. Typical signs of failure are circular, growing non-luminous areas, so-called "dark spots". The cause is often particle contamination during vapor deposition of the metal layers. The microscopic edges of the multilayer structure are also infiltrated by corrosion, which leads to a decrease in the effective luminous pixel area in screen applications.
相关新闻 换一批
-

翌光科技车载OLED尾灯亮相CINEVE 2025 助力新能源汽车智能化革新
2025-02-25
-

《中国改革报》专访胡永岚:“追光者”十年磨一剑
2025-01-20
-

《中国电子报》专访胡永岚:除了显示,OLED还能干啥?
2025-01-07
-

喜报!翌光科技被认定为河北省技术创新中心
2025-01-06






